Have you ever wondered about the significance of Edom in the Bible and its geographical location? Exploring the Map of Edom in the Bible can provide valuable insights into historical events, cultural context, and the journey of the Israelites. By understanding the geography of Edom as mentioned in the Scriptures, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the narratives and themes that unfold within the biblical text.
The Map of Edom in the Bible offers readers a visual representation of the lands associated with this ancient kingdom, allowing us to trace the movements of various biblical figures and understand the interactions between different nations. By delving into the geographical details of Edom, we can enhance our understanding of the context in which key events took place and the significance of certain locations mentioned in the Bible. Join us on a journey through the map of Edom as we uncover the rich tapestry of history and faith woven into the biblical narrative.
Exploring the Significance of the Map of Edom in the Bible
Map of Edom in the Bible
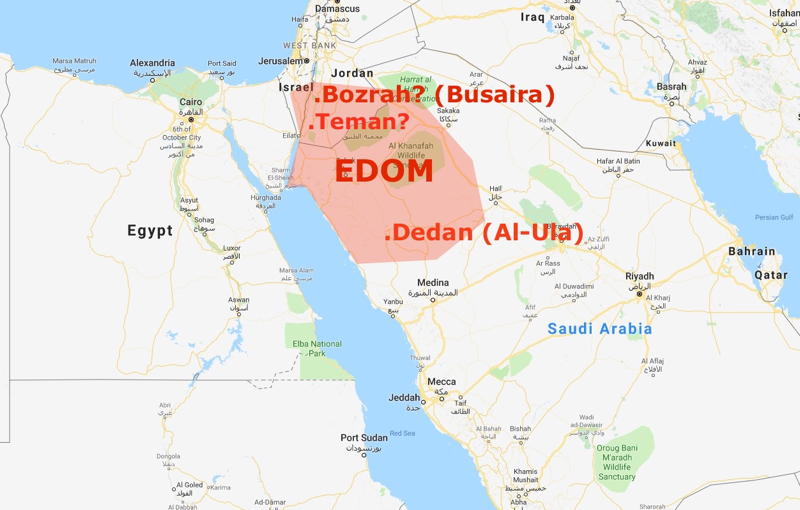
Edom, also known as Idumea, was an ancient kingdom located south of the Dead Sea in present-day Jordan. It was inhabited by the Edomites, descendants of Esau, the brother of Jacob in the Old Testament. The land of Edom held great strategic importance as it controlled vital trade routes connecting Egypt, Syria, and Arabia.
The boundaries of Edom varied throughout history but generally extended from the Zered River in the north to the Gulf of Aqaba in the south. To the west, it bordered the Arabah Valley, while to the east, it shared its boundary with the Arabian Desert. The rugged terrain of Edom consisted of rocky mountains, deep ravines, and vast plateaus, making it a formidable stronghold.
One of the most notable features of Edom was the ancient city of Petra, which served as its capital. Carved into rose-red cliffs, Petra was a marvel of engineering and architecture, featuring temples, tombs, and elaborate rock-cut facades. The city’s strategic location made it a bustling hub for trade and commerce, attracting merchants from far and wide.
Throughout the Bible, Edom is often mentioned in connection with the Israelites, with whom the Edomites had a complex relationship. The rivalry between the two nations dates back to the days of Jacob and Esau, whose conflict set the stage for generations of enmity. The Edomites refused passage to the Israelites during their exodus from Egypt, leading to tensions that persisted for centuries.
Several biblical prophecies foretold the fate of Edom, predicting its eventual downfall and desolation. The prophets Amos, Isaiah, and Obadiah all spoke of Edom’s judgment for its pride, violence, and mistreatment of the Israelites. Despite its once-mighty status, Edom eventually fell to the Babylonians and later to the Nabateans, fading into obscurity.
Today, the ancient kingdom of Edom lies in ruins, its once-glorious cities reduced to rubble. The land that was once home to fierce warriors and cunning traders now serves as a reminder of the transient nature of earthly kingdoms. Yet, the legacy of Edom lives on in the pages of the Bible, where its story is woven into the tapestry of Israel’s history.
Where is Edom on the map today?
Edom, mentioned in the Bible, was located in the southern part of present-day Jordan. It was bordered by Moab to the northeast, the Arabian Desert to the east, and the Gulf of Aqaba to the south. The capital of Edom was Bozrah, and it was known for its rocky terrain and strategic locations. Today, the region of Edom would roughly correspond to the southern region of Jordan, near the border with Saudi Arabia.
What nation is Edom today?
Edom in the Bible is believed to correspond to the region of modern-day Jordan. The descendants of Esau, who was also known as Edom, settled in the mountainous area southeast of the Dead Sea, which is part of present-day Jordan.
Where is Edom found in the Bible?
Edom is found in the Bible primarily in the Old Testament. It is a region located to the southeast of ancient Israel and was inhabited by the descendants of Esau, the brother of Jacob. The name “Edom” means “red” in Hebrew, referencing Esau’s red complexion at birth, for which he traded his birthright.
Important references to Edom in the Bible include:
1. The book of Genesis: Edom is first mentioned in Genesis 25:30 when Esau asks for food, giving up his birthright to Jacob.
2. The book of Numbers: The Israelites sought to pass through Edom on their journey to the Promised Land, but were denied passage (Numbers 20:14-21).
3. The book of Obadiah: The entire book is a prophecy against Edom for their arrogance and mistreatment of the Israelites.
4. The book of Ezekiel: Several chapters in Ezekiel also contain prophecies against Edom for their hostility towards Israel.
These are just a few examples of where Edom is mentioned in the Bible, illustrating its historical and theological significance in the context of the ancient Israelites.
What nationality are the Edomites?
The Edomites were a group of people who descended from Esau, the twin brother of Jacob in the Bible. They inhabited the region of Edom, which is located south of the Dead Sea in present-day Jordan. The Edomites were considered descendants of Esau and were often in conflict with the Israelites, who were the descendants of Jacob. In the Bible, the Edomites are portrayed as a distinct ethnic group with their own national identity.